Original Food and Sacred Medicines
Original Foods
“Original foods are plants or animals that are indigenous to the land, meaning they existed naturally on the land before settlers arrived. Food in the form of these plants, fruits, vegetables, or animals is a gift…Though our diets have changed significantly, the benefits of eating original foods remain the same. They are highly nutritious, which keeps us strong and healthy, and the hunting, fishing, trapping, and gathering of original food keeps us physically active and spiritually grounded. These are all parts of living a healthy life.”(NIDA, 2023)
Printable Food Resources
Sacred Medicines
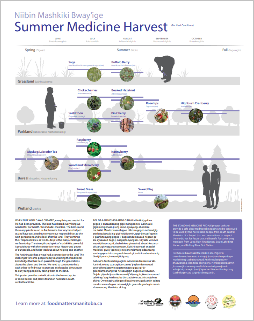
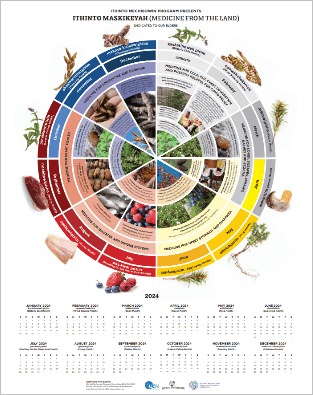
The four sacred medicines used in First Nations’ ceremonies are tobacco, sage, sweetgrass, and cedar. We have summarized the uses of the four sacred medicines below, but teachings on the sacred medicines vary from nation to nation and it is recommended that you learn more information from an Elder and/or Knowledge Keeper in your community.
- Tobacco – Tobacco is often used in smudging ceremonies and is seen as a tool for connecting to the spirit world. Tobacco is also presented as a gift during important ceremonies or before receiving a teaching – this practice is called a tobacco offering.
- Sage – Sage has cleansing properties and is used to purify spaces and people of negative energy, and invite positive and healing energy. Sage is used in smudging ceremonies, but can also be used in everyday life when you would like relief from internal struggles.
- Sweetgrass – Sweetgrass is known for its sweet aroma and represents sharing, caring, and love. It is also used in smudging ceremonies to bring harmony to the ceremony and aide in healing.
- Cedar – Cedar is considered a symbol of strength and serves as a shield from the unknown, bringing spiritual protection into ceremonies. Cedar is also used in teas for physical healing.
To print out a guide on the four sacred medicines and the medicine wheel, read the teachings and guidance provided by Knowledge Keeper Carolyn Moar.
Printable Medicine Resources